Excel Tricks: Calculate Cumulative Relative Frequency
Excel offers a range of tools to analyze data efficiently, and one powerful technique is calculating cumulative relative frequency. This method provides valuable insights by expressing the cumulative distribution of data, aiding in identifying patterns and trends. In this article, we will delve into the step-by-step process of calculating cumulative relative frequency in Excel, exploring its practical applications and benefits.
Understanding Cumulative Relative Frequency
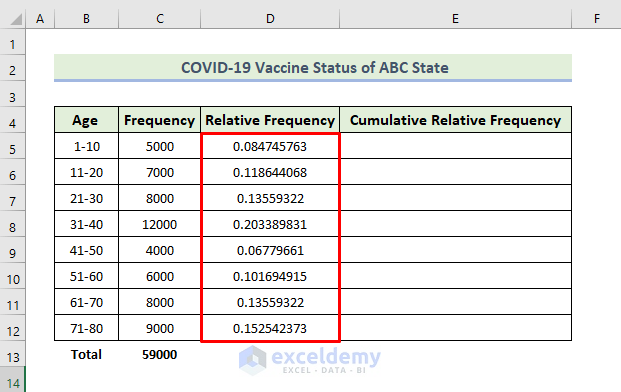
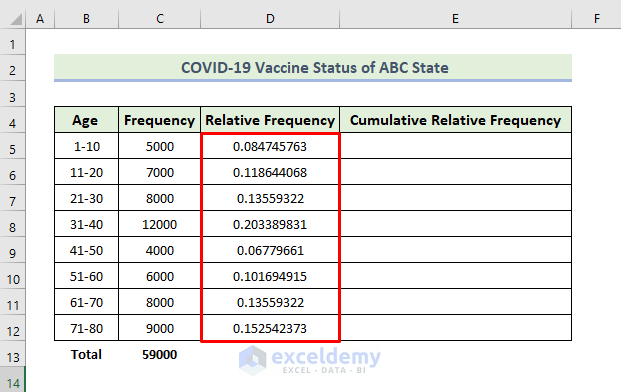
In the realm of data analysis, frequency distribution is a fundamental concept. It involves organizing data into groups or categories and counting the occurrences within each group. Relative frequency takes this a step further by expressing these counts as proportions or percentages, providing a more nuanced understanding of the data's distribution.
Cumulative relative frequency extends this concept by considering the cumulative sum of relative frequencies up to a specific point in the data set. It offers a powerful tool for identifying trends, patterns, and outliers, making it invaluable for various data-driven decisions and analyses.
To illustrate the concept, let's consider a simple example. Imagine we have a dataset representing the ages of a group of individuals. We can create a frequency distribution table, as shown below:
| Age Group | Frequency | Relative Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| 18-24 | 20 | 0.2 |
| 25-34 | 35 | 0.35 |
| 35-44 | 15 | 0.15 |
| 45-54 | 25 | 0.25 |
| 55-64 | 10 | 0.1 |
| 65-74 | 5 | 0.05 |
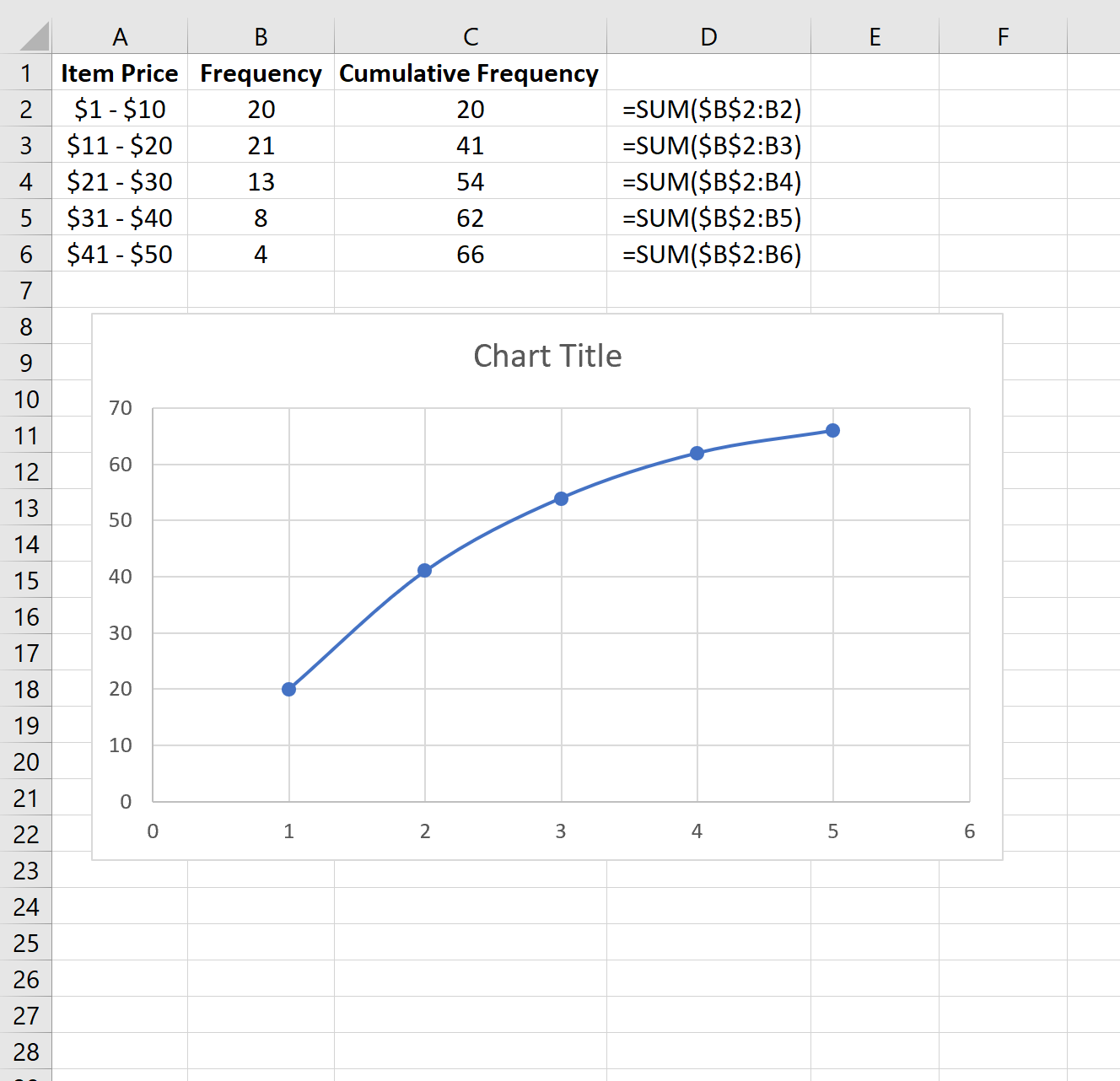
Now, let's calculate the cumulative relative frequency for this dataset. This will give us a clearer picture of how the age groups accumulate in terms of relative frequency.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Cumulative Relative Frequency in Excel

-
Prepare Your Data: Ensure your data is organized in a clean and consistent manner. In our example, we have age groups and their corresponding frequencies. It's crucial to have this data arranged in columns or rows for easy manipulation.
-
Calculate Relative Frequency: To calculate relative frequency, divide the frequency of each age group by the total number of observations. In Excel, you can use the formula
=Frequency/Total Frequencyfor each age group. This will provide a percentage representation of each age group's occurrence relative to the entire dataset. -
Insert a New Column: Create a new column adjacent to your frequency column. This will be where you calculate the cumulative relative frequency.
-
Use the SUM Function: In the first cell of your new column, enter the formula
=SUM(Relative Frequency), whereRelative Frequencyrefers to the cell containing the relative frequency for the first age group. This formula sums the relative frequencies of all age groups up to the current age group. -
Copy and Paste the Formula: Select the cell with the formula and drag the fill handle down to the remaining cells in the new column. Excel will automatically adjust the references in the formula to calculate the cumulative relative frequency for each age group.
At this point, your Excel sheet should now display the cumulative relative frequency for each age group, providing a comprehensive view of how the data accumulates.
Benefits and Applications of Cumulative Relative Frequency
Calculating cumulative relative frequency in Excel offers several advantages and practical applications:
-
Trend Identification: By visualizing the cumulative relative frequency, you can quickly identify trends and patterns in your data. It becomes evident where the majority of observations lie and how the data distribution evolves.
-
Decision-Making Support: Cumulative relative frequency is particularly useful for making informed decisions based on data. It helps identify outliers, understand the concentration of values, and determine the range of values that cover a significant portion of the data.
-
Quality Control: In manufacturing and quality assurance, cumulative relative frequency can aid in identifying defects or anomalies in production processes. It allows for the efficient monitoring of key metrics and the early detection of issues.
-
Market Research: Market researchers can utilize cumulative relative frequency to analyze consumer behavior, preferences, and demographics. It provides insights into the distribution of customer segments, helping businesses make data-driven decisions regarding product development, marketing strategies, and customer targeting.
-
Financial Analysis: In the financial sector, cumulative relative frequency is valuable for assessing investment performance, analyzing risk distributions, and understanding the concentration of returns. It aids in making strategic investment decisions and managing portfolios effectively.
The versatility of cumulative relative frequency makes it a powerful tool for data analysis across various industries and applications. By leveraging Excel's capabilities, you can efficiently calculate and interpret this metric, enhancing your data-driven decision-making process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Excel's ability to calculate cumulative relative frequency provides a comprehensive view of data distribution, allowing for informed decision-making and strategic planning. By following the step-by-step guide outlined in this article, you can unlock the insights hidden within your data, whether you're analyzing age groups, product sales, customer feedback, or any other dataset.
Remember, effective data analysis is a cornerstone of modern business success, and Excel's versatility and ease of use make it an indispensable tool for professionals across industries. So, dive into the world of data with confidence, armed with the knowledge of how to calculate cumulative relative frequency in Excel, and let your data tell its story.
With Excel's powerful features and your analytical prowess, you can transform raw data into actionable insights, driving innovation and growth in your field. So, embrace the power of cumulative relative frequency and take your data analysis skills to new heights.
How can I calculate cumulative relative frequency without using Excel?
+While Excel offers a convenient and efficient way to calculate cumulative relative frequency, it’s possible to perform the calculation manually. You can use a simple calculator or even pen and paper to add up the relative frequencies for each data point. However, manual calculations can be time-consuming and prone to errors, especially for large datasets. Excel provides an automated and error-free method, making it a preferred choice for data analysis tasks.
What is the difference between relative frequency and cumulative relative frequency?
+Relative frequency expresses the occurrence of a specific data point or category as a proportion or percentage of the entire dataset. On the other hand, cumulative relative frequency considers the cumulative sum of relative frequencies up to a specific data point. It provides a more comprehensive view of the data distribution, showing how the frequencies accumulate over time or across categories.
Can I visualize cumulative relative frequency in Excel?
+Absolutely! Excel provides various chart types that can effectively visualize cumulative relative frequency. One popular option is the cumulative area chart, which displays the accumulation of data over time or categories. Additionally, you can create custom charts or utilize Excel’s built-in charts to represent cumulative relative frequency in a visually appealing manner.
How can I use cumulative relative frequency in business analytics?
+Cumulative relative frequency is a valuable tool in business analytics, offering insights into customer behavior, market trends, and operational efficiency. For example, you can analyze sales data to identify the top-performing products or understand the distribution of customer age groups. This information can guide marketing strategies, product development, and customer segmentation, leading to more effective business decisions.
Are there any limitations to using cumulative relative frequency in data analysis?
+While cumulative relative frequency is a powerful tool, it’s essential to consider its limitations. It provides a summary of data distribution but may not capture individual data points’ intricacies. Additionally, the interpretation of cumulative relative frequency can be subjective, and the choice of data intervals or categories can impact the results. Therefore, it’s crucial to combine it with other analytical techniques for a comprehensive understanding of the data.